Enterprise Java Easy Readme to get started in J2EE
J2EE Getting Started Guide
Q.What is J2EE ?
Answer: server side specifications (APIs)
for different services such as Persistence,web comps(sevlets,JSP,filter) life -cycle management, EJB(Enterprise Java Bean) management,security,connection pooling,transactions ,JMS(Java Messaging Service), Java mail ,web services support ,JPA(Java persistence API) ,etc.
Why ???
1. Can support different types of clients(thin clnts ---web clnt or Thick clnts --appln clnt, mobile clnts
Thin clnt (min)--- only web browser + net conn. to server ---- protocol HTTP/HTTPS
Thick clnt (min) --- Java SE support + (optional) server lib + net cn to server
protocol --- RMI style protocol.(Server vendor propritery protocol based upon RMI/IIOP)
eg -- from core java ---TCP clnt,RMI clnt,UDP clnt
2. Server side applications ---- will be completely independent of underlying web server/application server.(J2EE compliant server)
3. Enterprise applications -- distributed, transactional, and portable
applications that leverage the speed, security, and reliability of server-side technology.
As application server or web server provides ready made implementation of primary services , it frees server side developer from developing system level services(eg ---Naming , Security,Transactions, connection pooling,persistence,mesaging,mail,web services ....). --- so that developer can concentrate on B.L(Business logic)
Developing web applications
On server side --- (min) --- web server(j2ee compliant)
HTTP Server/web server --- combination of server HOST & server process.
Def port NO - 8080(9090)
Job --- Receive HTTP requests , service the same and generate HTTP response, send the same to web clnt.
Settings ---
0. set path : 1st entry jdk7\bin &
set 1. JAVA_HOME : <jdk1.7 install dir>
2. set TOMCAT_HOME : <Tomcat install dir.>
3. Optional --- set CATALINA_HOME to <Tomcat install dir.>
4. set classpath to servlet-api.jar
Steps of creating web-application in side the web server
1. Create J2EE compliant web application folder structure.(location-- hot deployment folder)
2. Add HTML content under root & test it with URL---
http://localhost:9090/test_web/welcome.html
3. How to add welcome file list under web.xml?
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
Request URL
http://www.abc.com:9090/test_web/
Concept --- How web server will service this req & add HTML content in HTTP response?
What is Web container --- (WC) & its jobs
 |
| Web container |
Its run-time env for dyn web components(Servlet & JSP,Filter) .
Jobs ---
1. Creating Http Request & Http response objects
2. Controlling life-cycle of web comps
3. Giving ready-made support for services --- Naming,security,Conn pooling
Version Details : web -application 3.X
page 82 -- for web application request -response overview.
page 85 -- web module structure
Why servlets --- to add dynamic nature to web application.
Introduction to Servlets
What are servlets ? --- server side dyn. web component residing within web appln from within web-container.
Java classes : no main method & consists of overriding form life-cycle methods.(init,service,destroy) --- prog's job
Invocation of the life-cycle methods : done automatically by WC.
Servlets will reside within the WC in one of the web-applns. They are never downloaded on the clnt machines(unlike the applets)
Typically : servlets will contain :
1. Rq. processing logic
2. Business logic(B.L)
3. dyn. resp. generation logic.
4. Page navigation logic
5. data access logic
Objective :
generate a welcome msg from the servlet ---with changing time stamp
Steps for Sevlet creation & deployment
0. set path : 1st entry jdk1.7\bin & set JAVA_HOME : jdk1.7, set TOMCAT_HOME : Tomcat install dir.
1. set classpath to servlet-api.jar
HOW ?
set classpath=<Tomcat install dir>\lib\servlet-api.jar;
--- imple. classes
for Servlet API . ---Servlet specs (i/f) will be sun supplied & imple. classes suppiled by server vendors.
2. From <src> create .java src for Servlet.
2.1 To genrate the dyn. resp from the servlet :
(life-cycle methods : init,service,destroy)
Reference : javax.servlet.Servlet(i/f) ---> life-cycle methods.---> impl. class javax.servlet.GenericServlet : protocol inde. servlets.---> sub-classed by the javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet : It is used for creating HTTP proto. specfic servlets
Servlet prog. must override : (def. method=get)
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest rq,HttpServletResponse rs) throws ServletException,IOException
who invokes doGet : WC
how many times : once per clnt rq.(via a thrd created by the WC)
prog job : @Override doGet
3. Compile & place the classes in <web-inf>/classes
4.Add the Deployment steps(xml tags) to the web.xml(deployment desc)
Register the servlet or make the servlet entry in web.xml
Per servlet :
<servlet>
<servlet-name>abc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class> ex.FirstServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>abc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
Meaning ---
1. url-pattern --- / ---as it appears in URL sent by clnt. -- after web context path
2. servlet-name --- meant for WC --- alias or internal name of the servlet.
3. servlet-class---F.Q servlet class name
URL sent by the clnt : http://localhost:9090/test_web/hello
5.Run clnt
Life-cycle of the servlet
 |
Life-cycle of the servlet |
2.After resolving till http://www.abc.com:8080/testweb : the clnt req. reaches the top of ur web appln(i.e testweb)
3. WC opens web.xml : serches for matching url-pattern --- from url-pattern get the servlet-name(i.e servlet alias) ----from the servlet-name find the F.Q class name of the servlet class.
4. WC will try to load the servlet class from web-inf/classes folder & instantiate the same.(def. constr)
5. WC invokes public void init(ServletConfig sc) throws ServletException method : & inits the servlet. (Prog job : to specify all 1time jobs eg : DB conn, creation of PST)
6. If servlet's init method throws the SE : then WC will mark the servlet unavailable for any clnts.
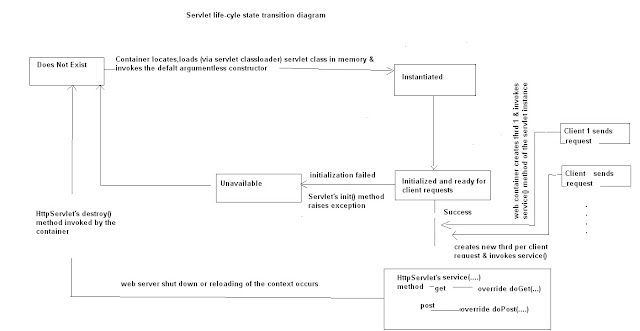
7. If init method succeeds : WC(ie. JVM within the web srvr) will create a thrd . Thrd is created per each clnt req. & thrd in its run() will invoke the service(rq,rs) of the servlet class.
8. HttpServlet(i.e the super-class) has overridden the service method : checks the method by which data is sent by the clnt eg: get,post,options,head,delete & corro. it will invoke the matching method : doGet,doPost,doHead, ......
9. Prog job : override the matching method : will contain req. processing , B.L.... & resp generation logic.
10. When doGet rets : thread becomes dead : BUT the servlet instance persists in the mem. of the WC
11. Either when the context(i.e web-appln) is getting re-deployed or un-deployed or server is shutting down : WC will invoke the public void destroy() of the servlet class & THEN the servlet instance will be GCed.
 |
| servlet Example |
From Java EE 6
Annotation support is available to Servlets.
1. @WebServlet
Class level annotation used to declare a servlet.
Who processes it ? Web container
When -- at deployment time,
Effect -- Corresponding servlet is made available at the specified URL patterns.
eg -- @WebServlet("/hello")--- URL pattern used is /hello
public class MyServlet extends HS{.....}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = { "/test" ,"/abc"},loadOnStartup=1) --- Can be invoked using any of the URL patterns /test or /abc . This servlet will loaded & inited at the context start-up time.
@WebServlet(urlPatterns ={ "/test1"},initParams={@WebInitParam(name="aa",value="cc"),@WebInitParam(name="bb",value="dd")}) --- URL pattern for this servlet is /test1, 2 init params --- aa & bb with vals cc & dd
IDE steps : for Eclipse
1. stop tomcat apache web server.(external)
2. Add server.(New Server : specify the Tomcat install dir) & change it to J2EE perspective
& from Server tab --- add new srvr.
3.Create new web appln : Dyn web proj & add the HTML/JSP content in webContent folder & servlets (using new--> servlet option) unde Java src.
WebContent ---> root of ur web-appln --- to place html , jsp, applet
src : for java sources.
web-inf ---> web.xml
4. For running the HTML --> can specify directly "Run On Server" option.
obj : attach the HTML form & submit the same to the servlet.
Objective : attach the HTML form, accept the user name & generate : personalized Hello.
HttpServletRequest(sub interface of ServletRequest) API for rq. processing
1. API of ServletRequest
Method : String getParameter(String pName) --- rets pValue.
Usage --- String val=rq.getParameter("f1");
Objective : print all rq param nms & their vals
2.Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap() --- key -- pName , val -Pval[]
(array based values : ie. one pName can have multiple PVals eg --- multiple selected checkbox or multiple selction list)
3. String[] getParameterValues(String pName) --- rets vals associated with pName --typically used multiple chk boxes or multiple selectable lists.
4. Enumeration<String> getParameterNames()
Rets : enumeration(i/f similar to Iterator) of param names
-----------------------------
How to pass init-params to the servlet?
1. Add the init-params to web.xml from within the servlet tag.--- they represent servlet sepcific params.(For adding global params to all servlets - from the same web-appln : tag used is <context-param>....will be used later)
eg ---
<servlet>
<servlet-name>init</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>ex.TestInitParam</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<description>token init param</description>
<param-name>test</param-name>
<param-value>test_data</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>init</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/test_init</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
2.
javax.servlet.ServletConfig --- represents the i/f to store servlet's init params. Will be used by WC before init --- to add all servlet specific init-params
To use the init-params
1. Override the init() --- public void init() throws SE
1.1 Get ServletConfig ref.
ServletConfig getServletConfig()
1.2 Get the init params from ServletConfig
API : javax.servlet.ServletConfig
String getInitparameter(String paramName) : rets the param value.
JDBC-Servlet(DB contacting servlet)
IMP : copy JDBC drvr JAR either to ur <Tomcat_home>/lib : to share it among all the web-applns or atleast copy it to ur web-appln's <web-inf>/lib
To Add the servlet specific init params : (eg : DB conn. params : drvr cls,dbURL,uName,pass)
Add the <init-param> tag within the <servlet> tag
NOTE : These params are specific to a single servlet : not globally shared among all the servlets(For gloabal param : u have <context-param> : will be discussed later.....)
To use the init-params
1. Overrider the init()
1.1 Get the init params from ServletConfig
API : javax.servlet.ServletConfig
String getInitparameter(String paramName) : rets the param value.
1.2 Register the DB drvr
1.3 get Connection
1.4 create PST
1.5 wrap the init() within try-catch ---> in case of any exc : wrap the exc in ServletExc & re-throw the same to WC.
Objective : User(client) specifies the ID from the HTML form ---> form gets submitted to the UserServlet . Validates user from db Servlet chks if user exists : if yes ---> displays the dtls to the user o.w gives : Retry Link.
Objective ---
User(client) specifies the ID from the HTML form ---> form gets submitted to the UserDBServlet . It must have cn to DB . Servlet chks if user exists : if yes ---> get the dtls from the underlyng DB & redirects the user to the next page(eg : emp dtls page, BankAccount main page, catalog page, or stock dtls page....) & displays the user details from the 2nd page (w/o re-connecting to the DB) . U must be able to remember & identify the user throughout the entire web-appln .In case of failure : retry link as before.
What is the need of session tracking?
HTTP : stateless-- by default ( as it sits over TCP/IP : so sending rq. from the user ,rq processing ,B.L & finally sending the resp. to the user : involves : TCP-IP cn established, data xfer & cn closed.)
To make HTTP stateful : use session tracking techniques.
Need : 1. To identify the clnt among multiple clnts
2. To remember the conversational state of the clnt(eg : list of the purchased books/ shopping cart) throughout current session
session = all requests coming from same clnt from login to logout or till session expiration tmout.
session tracking techniques
1. Plain cookie based approach :
2. HttpSession based approach (internally relying on a cookie : JSessionID)
3. HttpSession + URL rewriting
Regarding cookies
What is a cookie?
Cookie is small amount of text data.
Created by -- server (servlet or JSP prog) & downloaded (sent) to clnt browser---within response header
Cookie represents data shared across multiple dyn pages from the SAME web appln.
1 & 2 will fail to track(remember) the clnt : if clnt browser rejects the cookies from the web server.
3: will continue to work inde. of clnt browser settings.
1. Plain cookie based approach :
Steps :
1. Create cookie/s instance/s
javax.servlet.http.Cookie(String cName,String cVal)
2.Add the cookie/s to the resp hdr.
HttpServletResponse API :
void addCookie(Cookie c)
3. To retrieve the cookies :
HttpServletRequest :
Cookie[] getCookies()
4.Cookie class methods :
String getName()
String getValue()
void setMaxAge(int age)
int getMaxAge()
Disadvantages of pure cookie based scenario
1. Cookies can handle only text data : storing Java obj or bin data difficult.
2. As no of cookies inc., it will result into increased net traffic.
3. In cookie based approach : entire state of the clnt is saved on the clnt side. If the clnt browser rejects the cookies: state will be lost : session tracking fails
Technique # 2 : Session tracking based on HttpSession API
session scoped attributes(i.e Java objs created on the server side) are shared among all the dyn web pages(ie. servlet/JSP) participating in session tracking --> ie where HttpSession is enabled by calling req.getSession() : for JSP no such need : enabled as a default.
-----------------------
Prog Invokes :
1. HttpServletRequest API
HttpSession getSession();
Internally WC invokes the follow.
1.1 WC chks if u are a new or old user(by chking : rq.getCookies()---> cookie[] : null=> new user. If non-null : it will chk : c.getName().equals("JSESSIONID") : if exists : extracts the cookie val : c.getValue() : JsessionID's unique value)
1.2 If u are new user
a> : WC creates a single cookie(JSessionID, string val : unique per clnt)
b> WC adds the cookie to resp hdr.
c> Creates the Data structure : (HM) : empty : to store the session attributes(attr =server side java obj : with string name) -- HttpSession obj
d> Rets the HttpSession obj ref to the prog.
1.3 If u are old user :
WC will retrieve the HTTPSession obj : by using the JsesionID val & ret the existing Http Session ref to the prog.
Simplified steps for HttpSession based session tracking.
1. Create new Http Session or retrieve existing session
API
HttpServletRequest ---
HttpSession getSession()
Above method creates NEW HTTP session obj for new user or returns existing HTTP session object for old user.
HttpSession --- i/f from javax.servlet.http
2. : How to save data in HttpSession?(scope=entire session)
API : HttpSession
public void setAttribute(String attrName,Object attrVal)
3. For retrieving session data(getting attributes)
public Object getAttribute(String attrName)
4. To get session ID
String getId()
5. How to invalidate session?
HttpSession API
public void invalidate()
Note -- attribute = server side object
attribute --- attr name(String) & attr value (java.lang.Object)
Attributes can exist in one of 3 scopes --- req. scope,session scope or application scope
1. Meaning of req scoped attr = attribute is visible for current req.
2. Meaning of session scoped attr = attribute is visible for current session.
3. Meaning of application scoped attr = attribute is visible for current web appln.
---------------------
Simplified steps in Session Tracking via javax.servlet.http.HttpSession --i/f
1. Get Http Session from WC
API of HttpServletRequest
public HttpSession getSession()
WC -- will either create NEW Http Session obj or will continue with the existing object.(HttpSession object is created on server side heap)
2. How to add data(clnt's conversational state) to session scope?
attribute --- server side object , created by server side dev(Servlet/JSP)
attribute --- distinct name (String)
value -- Object
attributes can be stored under ANY(request | session | application) scope.
public void setAttribute(String attrName,Object attrVal)
3. How to get data from session scope?
public Object getAttribute(String attrName)
4. How to invalidate or discard session?
HttpSession API
void invalidate()
How to redirect the clnt from page to page (next page could be from same web appln , or diff web appln on same server or any web page on any srvr) : using clnt pull tech.
API : HttpServletResponse method
void sendRedirect(String redirectUrl)
redirectUrl : URL of the next page.
Objective : session tracking should work irrespective of the clnt browser setting(i.e with or w/o cookie support)
Session Tracking tchnique :
3. HttpSession + URL rewriting
For tracking the clnt (clnt's session) : the only info WC need from the clnt browser is JSessionID value. If clnt browser is not sending it using cookie : Servlet/JSP prog can embed the JSessionID info in each outgoing URL .
What is URL Rewriting : Encoding the URL to contain the JSEssionID info.
W.C always 1st chks if JsessionID is coming from cookie, if not ---> then it will chk in URL : if it finds JseesionID from the encoded URL : extracts its value & proceeds in the same manner as earlier.
API :
For URLs generated by clicking link/buttons(clnt pull I) use
HttpServletResponse method
public String encodeURL(String origURL)
Rets : origURL;JSESSIONID=12345
For URLs generated by sendRedirect : clnt pull II : use
HttpServletResponse method
public String encodeRedirectURL(String redirectURL)
Rets : redirectURL;JSESSIONID=12345
Server pull : technique for navigating the user to next page IN THE SAME REQUEST.
R.D (Request Dispatcher) : represents the dynamically chained resources(typically JSPs/servlets)
Forward scenario of the Request Dispatcher(i/f from javax.servlet pkg)
steps of Implementation
1.
Create the Request Dispatcher object
API : ServletRequest : method
RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String dispatcherURL)
dispatcherURL : eg : /details => / implies root of ur web-appln.
eg : /details
2. Chk if R.D is not null---> then invoke the forward(...)
API : RequestDispatcher method
void forward(ServletRequest rq,ServletResponse rs)
For RD's include scenario-
replace forward by include.
Among the following which all will be thrd safe attributes/vars ?
1. Servlet's instance data members : unsafe
2. Servlet's method local vars : safe
3. session scoped attributes : safe between 2 rqs coming from diff. clnts.
4. request scoped attributes : safe
5. Context scoped attributes : highly unsafe.
I set : db.html---> DBServlet.java(servlet+jdbc)
Session Tracking Techniques
1. Cookie based scenario
II set : db_cookie.html ---> DBServletCookie.java (servlet+jdbc + redirection+cookie based session tracking)
B.L : If Emp id is found (db servlet) ---> redirect the user to Details Page(DetailsServlet) & from Details Page : disp emp dtls.
Session tracking : via HttpSession(i/f : javax.servlet.http) API
First 2 dis . adv of cookie based scenario are removed , prog jobs are reduced & entire clnt state (excluding JSessionID) will be saved on the server side .
2. HttpSession based scenario
IIIset : db_session.html ---> DBServletSession.java (servlet+jdbc + redirection+HttpSession based session tracking) ---> DetailsServletSession.java
Note ---
How to ensure that servlets are located/loaded/inst/inited --- at the time of web context start-up?
Add <load-onstartup> tag --- in servlet tag -- to specify order of loading
 |
| J2EE Compliant Web application Structure |

Comments
Post a Comment